Bus
Bus network topology
- In local area networks where bus topology is used, each machine is connected to a single cable. Each computer or server is connected to the single bus cable through some kind of connector. A terminator is required at each end of the bus cable to prevent the signal from bouncing back and forth on the bus cable.
Star
Star network topology
In local area networks with a star topology, each network host is connected to a central hub. In contrast to the bus topology, the star topology connects each node to the hub with a point-to-point connection. All traffic that transverses the network passes through the central hub. The hub acts as a signal booster or repeater.
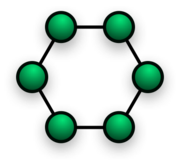
Ring
Ring network topology
- In local area networks where the ring topology is used, each computer is connected to the network in a closed loop or ring. Each machine or computer has a unique address that is used for identification purposes. The signal passes through each machine or computer connected to the ring in one direction. Ring topologies typically utilize a token passing scheme, used to control access to the network.
Mesh
The value of fully meshed networks is proportional to the exponent of the number of subscribers, assuming that communicating groups of any two endpoints, up to and including all the endpoints, is approximated by Reed's Law.
Fully connected mesh topology
Tree
Tree network topology
Also known as a hierarchical network.
The type of network topology in which a central 'root' node (the top level of the hierarchy) is connected to one or more other nodes that are one level lower in the hierarchy (i.e., the second level) with a point-to-point link between each of the second level nodes and the top level central 'root' node, while each of the second level nodes that are connected to the top level central 'root' node will also have one or more other nodes that are one level lower in the hierarchy (i.e., the third level) connected to it, also with a point-to-point link,






No comments:
Post a Comment